Presentation and key elements
What is it?
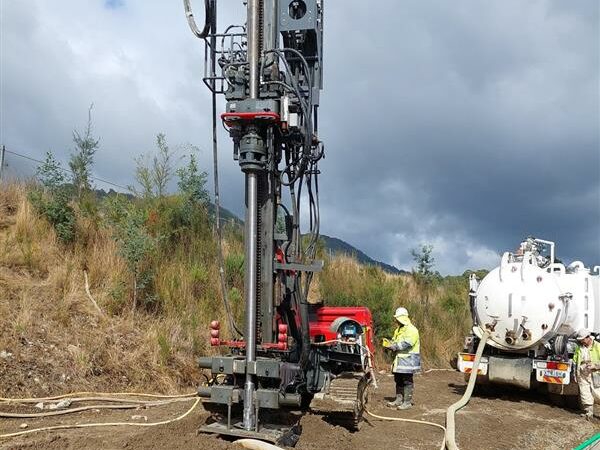
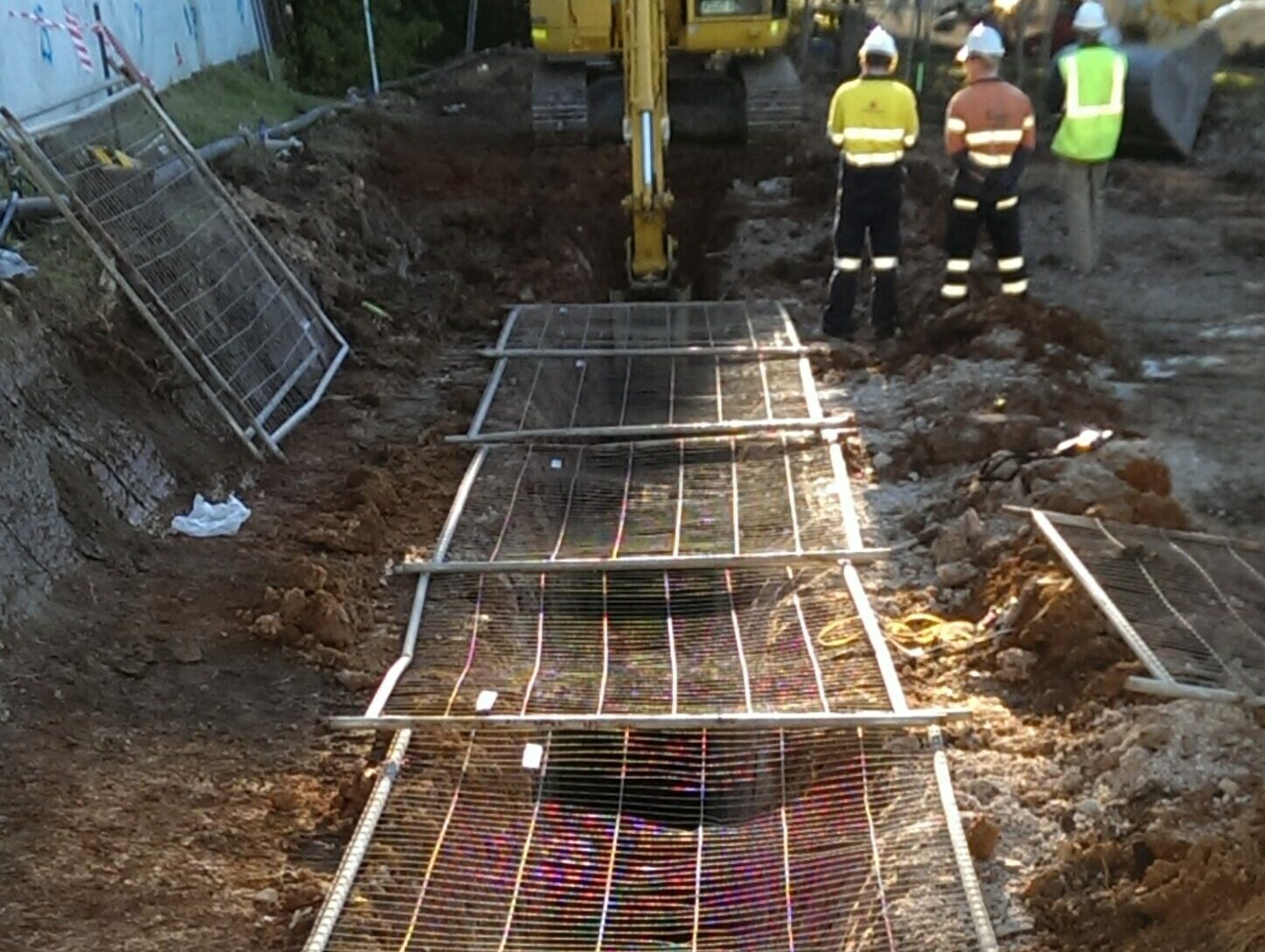
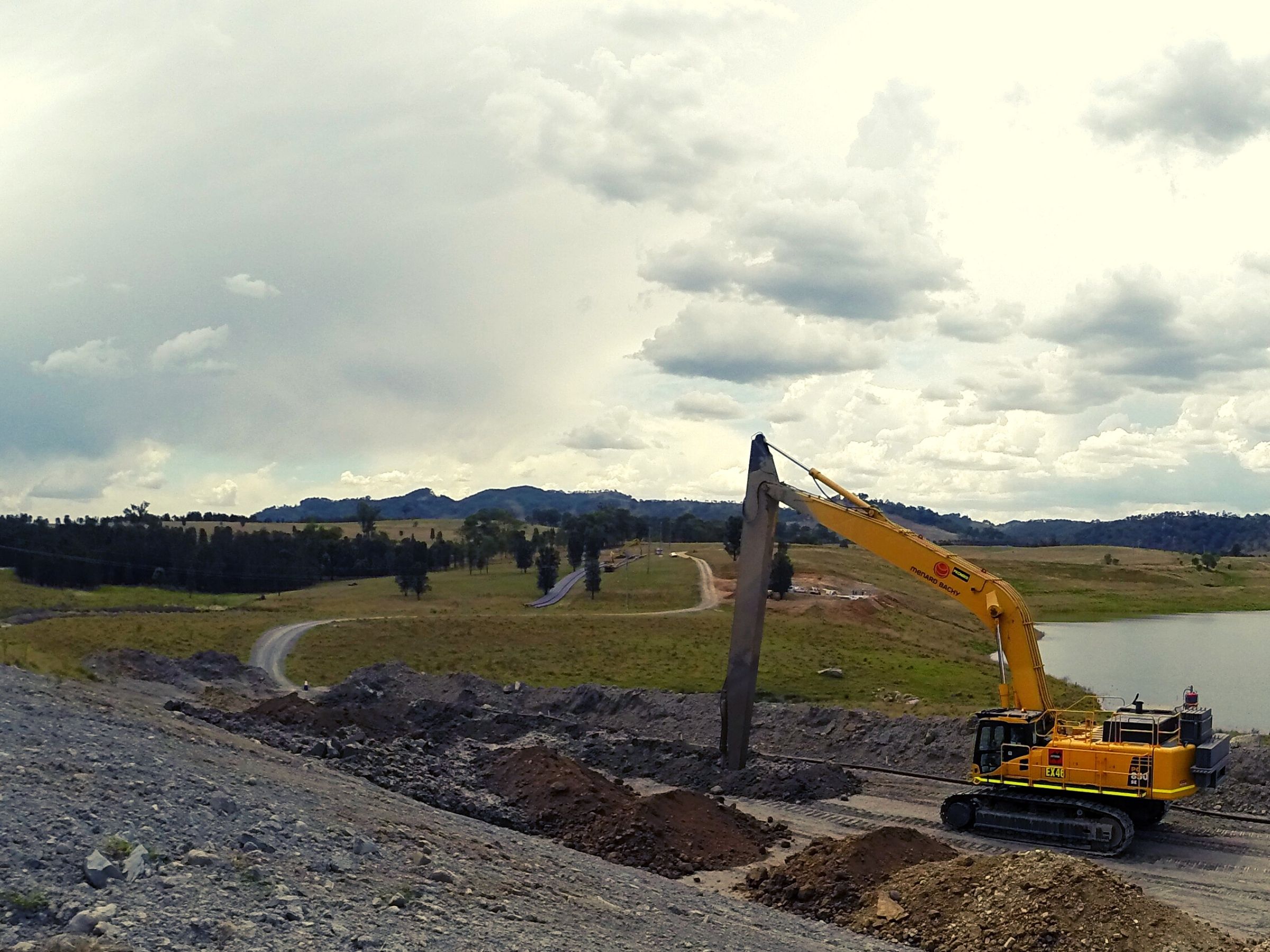
Slurry walls are non-structural subsurface elements that could be either used for stiffening the ground or creating barriers with specific hydraulic and permeability characteristics. First, a trench is excavated under slurry, which provides lateral stability of the trench. In the case of cement-bentonite walls the fluid slurry that contains cement and bentonite will set and form the permanent element; however, in all other cases the slurry is replaced with a specially designed and mixed backfill. For cut-off walls the backfill consists of a homogeneous mix of excavated soil, bentonite slurry, clay and sometimes cement. For permeable barriers the trench is backfilled with a permeable material and may include special products to neutralise contaminants.
When and why use it?
Slurry walls can be used on a wide range of applications applicable to groundwater related issues. These walls are a fast and cost effective method to contain, divert or intercept groundwater. These techniques have been implemented to manage a wide range of water-borne contaminants and complex water chemistry environments.
💡 Menard’s tip
Slurry walls have been installed to depth of approximately 50 m. Soil- bentonite slurry walls create reduced volumes of spoil because excavated material is reused as backfill material.